In modern industrial and construction applications, galvanized steel coils have become the material of choice for many manufacturers and international buyers due to their excellent corrosion resistance, good process-ability, and high cost-effectiveness. This article will introduce galvanized steel coils from the perspectives of product performance characteristics, primary application scenarios, and procurement recommendations.

1.What are galvanized steel coils?
Galvanized steel coils are metal materials produced by coating the surface of ordinary cold-rolled or hot-rolled steel strips with a layer of zinc to enhance their corrosion resistance. Depending on the production process, they are primarily categorized into two types: hot-dip galvanized and electro galvanized.

Hot-dip galvanized steel coils: Steel is immersed in molten zinc at high temperatures, where zinc reacts metallurgically with the steel to form a uniform and dense zinc layer. This coating is thick, has strong adhesion, excellent weather resistance, and a long service life.
Electro galvanized steel coils: A zinc layer is formed on the steel surface through electrolysis. The zinc layer is thinner, with a high surface finish, making it suitable for interior components or electrical parts with high precision requirements or applications with high aesthetic standards.
The zinc layer not only prevents air and moisture from contacting the base material but also serves as a “sacrificial anode,” providing some self-protective functionality even if the steel surface is scratched.
In summary, galvanized steel coils = ordinary steel coils + corrosion-resistant “protective layer.”
2.Technical Origins and Historical Background of Galvanized Steel Coils
Galvanized steel coils are a widely used corrosion-resistant metal material in modern industry.
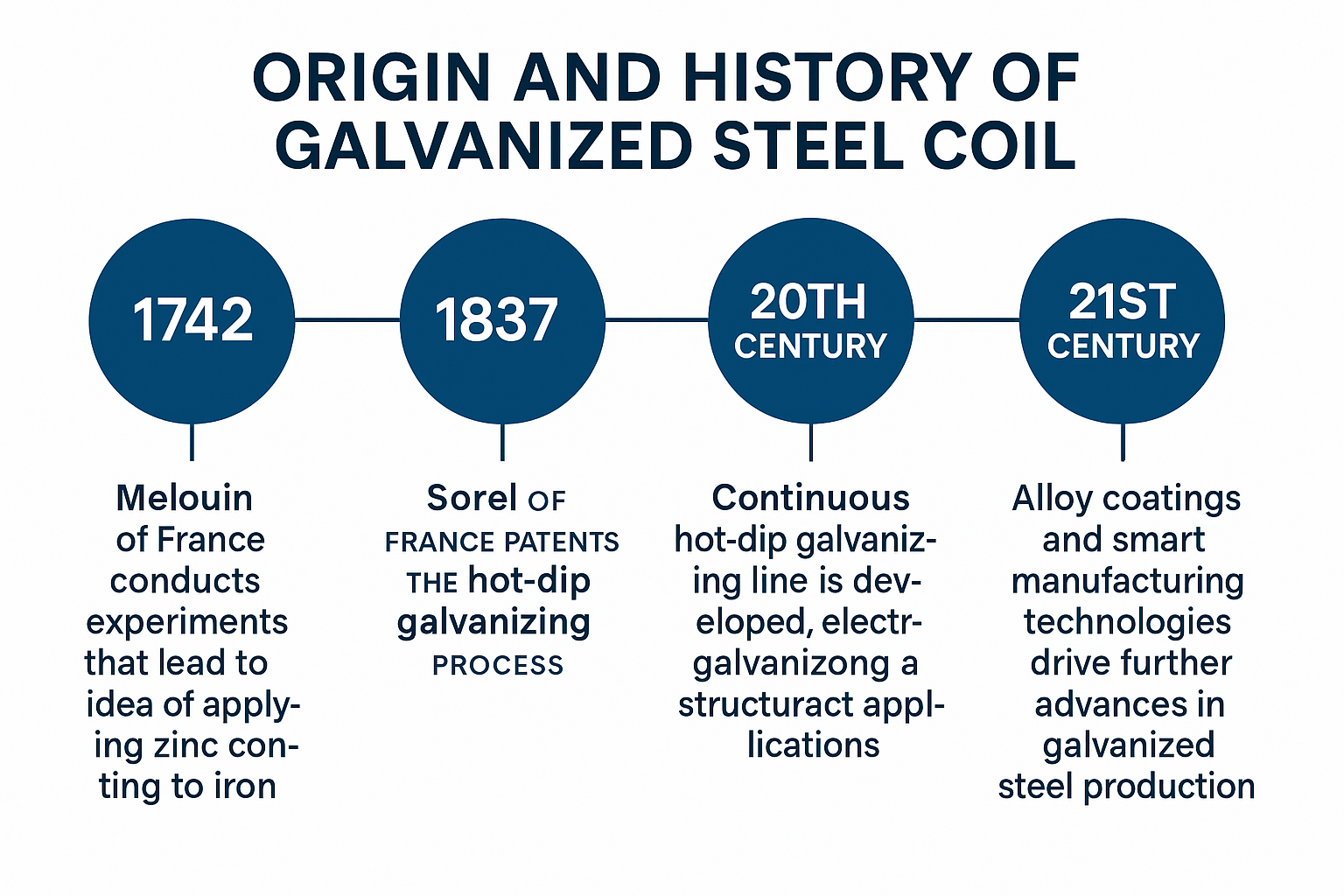
As early as the 18th century, French chemist Melouin first proposed the idea of immersing iron in molten zinc for protective coating in 1742. This experiment revealed zinc’s role in preventing metal oxidation, marking the beginning of the hot-dip galvanizing process. In 1837, French engineer Sorel successfully obtained the first hot-dip galvanizing patent, signifying the formal industrialization of the technology.
From the late 19th century to the early 20th century, hot-dip galvanized iron sheets began to be widely used in building infrastructure such as roofs, fences, and water pipes. However, during this period, galvanizing was primarily performed manually on individual pieces, resulting in limited production capacity and low processing efficiency. It was not until the 1950s and 1960s, with the emergence of continuous hot-dip galvanizing production lines, that steel strips could be continuously galvanized, cooled, and coiled on high-speed production lines, marking the true birth of galvanized steel coils.
In the 1980s, electro galvanizing technology began to gain traction. This process uses electrolysis to deposit a uniform zinc layer on the surface of steel, though the coating is thin, it offers a smooth surface and is easy to paint, making it widely used in industries with high aesthetic requirements, such as automobiles and home appliances.
In the 21st century, alloy coatings (such as zinc-aluminum-magnesium) and intelligent production technologies have continued to drive the evolution of galvanized steel coils toward higher performance and greater environmental friendliness.
Today, galvanized steel coils are widely used in industries such as construction, automotive, home appliances, and photovoltaics, becoming an indispensable basic material in the global manufacturing system.
3.Core Advantages of Galvanized Steel Coils
A.Excellent Corrosion Resistance
Zinc is a metal with strong corrosion resistance and also provides “sacrificial anode” protection: even if the zinc coating on the surface is damaged, it can still protect the steel substrate from corrosion through electro chemical action.
B.Good Formability and Weldability
Galvanized steel coils offer excellent form-ability and weld-ability, making them suitable for various post-processing operations such as stamping, shearing, bending, and coating, facilitating customers’ deep processing applications.
C.High Cost-Effectiveness
Compared to corrosion-resistant materials like stainless steel and aluminum alloys, galvanized steel coils offer a more cost-effective advantage. They have low maintenance costs and a long service life, making them an important cost-saving measure in industrial applications.
D.Aesthetically Pleasing Surface with Decorative Properties
Thanks to the excellent adhesion and processing performance of its zinc coating, galvanized steel coils are highly compatible with various surface treatment technologies, such as color coating, spraying, painting, and film coating.
E.Wide range of customizable specifications
Based on different national standards and steel grades, we offer thicknesses ranging from 0.12 to 25 mm and widths from 50 to 1,250 mm to meet the needs of different markets and industries.
4.Typical application scenarios for galvanized steel coils
A.Building structures and roofing systems
Galvanized steel coils perform exceptionally well in steel structure factories, warehouse roofs, and wall decoration panels, particularly suitable for long-term use in humid, coastal, and highly corrosive environments.
B.Transportation and Municipal Facilities
Used for manufacturing highway sound barriers, guardrail panels, traffic signs, and light poles, where materials must be both high-strength and weather-resistant, galvanized steel coils are fully capable of meeting these requirements.
C.Appliance Housings and the White Goods Industry
Refrigerator, washing machine, and air conditioner housings demand extremely high standards for surface quality and processing performance. Galvanized steel coils are highly favored for their smooth and delicate surface finish.
D.Agricultural and Livestock Facilities
For example, chicken coops, pigsties, and greenhouse frameworks are exposed to manure or moisture for extended periods. Using galvanized steel significantly extends their service life.
E.Automotive Manufacturing
Components such as vehicle chassis, door panels, fuel tank housings, and structural frames use galvanized steel sheets in some vehicle models to enhance corrosion resistance and safety.
Galvanized steel coils, with their excellent oxidation resistance and structural strength, have penetrated multiple industrial sectors and become a foundational material in modern manufacturing.
5.Tips for purchasing galvanized steel coils
Galvanized layer quality: High-quality galvanized steel coils should have a galvanized layer thickness that meets standards, which can be tested using a thickness gauge. The higher the thickness, the better the corrosion resistance.
Galvanized layer uniformity: The surface of high-quality galvanized steel coils should be smooth, with no obvious zinc nodules, black spots, rust spots, or other defects.
Base Material Properties: The steel base should have good yield strength and ductility, with no folds or cracks.
Processing Performance: It should be able to withstand processes such as shearing, bending, and stamping without cracking. It should also have good compatibility with surface treatments like painting and coating, with strong adhesion.
Corrosion Resistance: Its corrosion resistance can be tested using a neutral salt spray test (NSS).
Inspection Reports: Complete quality inspection reports should be provided.

